The Ultimate Guide to Restaurant Lingo: FOH, BOH, Restaurant Technology and Operations

Running a restaurant means speaking a language all on its own. From front of house (FOH) callouts to back of house (BOH) prep shorthand, and now, a growing list of restaurant technology terms tied to online ordering, delivery, and POS integrations, these phrases show up every shift.
This restaurant terms glossary breaks down the most common restaurant lingo in plain language, with quick definitions and real-world context so owners, managers, and staff can stay aligned, train faster, and avoid miscommunication during service.
Use it as a reference for day-to-day operations, onboarding new hires, and understanding the tech and processes that keep your restaurant’s orders moving smoothly.
Restaurant Technology Terms

Online ordering system
- Definition: A tool that lets guests place pickup or delivery orders online through your website, app, or link.
- Example: “We turned on online ordering so guests can place takeout orders without calling the host stand.”
- Why it matters: It reduces phone pressure, captures more orders, and helps you control the guest experience.
First party ordering (direct ordering)
- Definition: Orders placed directly with your restaurant, not through a third party marketplace.
- Example: “We encourage guests to order through our direct ordering link so we keep the relationship.”
- Why it matters: Direct ordering supports customer data ownership and helps protect margins. For a deeper breakdown of direct vs third party ordering, check out our guide on increasing customer loyalty.
Third party ordering
- Definition: Orders placed through a marketplace that lists many restaurants and charges fees.
- Example: “We get orders from third party ordering (marketplace apps), but it’s harder to build repeat business there.”
- Why it matters: Marketplaces can add volume, but they often come with commission fees and limited diner relationships.
Commission fees (marketplace commissions)
- Definition: The percentage or flat fees charged by third party ordering marketplaces on each order.
- Example: “We’re often charged 15-30% in commission fees on third party delivery apps.”
- Why it matters: Fees can quietly eat into profitability, especially on high volume takeout nights.
Customer data ownership
- Definition: Who controls guest details like email, phone number, and ordering history.
- Example: “When guests order through direct ordering, we own the customer data and can follow up, reward them, and encourage them to come back.”
- Why it matters: Owning your customer data makes it easier to market without relying only on social algorithms.
Branded ordering app
- Definition: A mobile app with your restaurant name and branding that guests use to order directly.
- Example: “Regulars use our branded ordering app for quick reorders.”
- Why it matters: It keeps your brand front and center, avoids commissions, and makes repeat ordering easier.
POS integration
- Definition: An integration between your online ordering and your point of sale so orders flow into one system.
- Example: “Because of our new POS Integration, orders now hit the POS automatically instead of being manually inputted.”
- Why it matters: It reduces manual entry, minimizes mistakes, and speeds up service.
Order aggregation (tablet consolidation)
- Definition: A setup that pulls orders from multiple ordering channels into one place, such as a one single tablet.
- Example: “Instead of three tablets, we use order aggregation to manage everything coming in from one view.”
- Why it matters: Fewer devices means fewer missed tickets and a calmer shift.
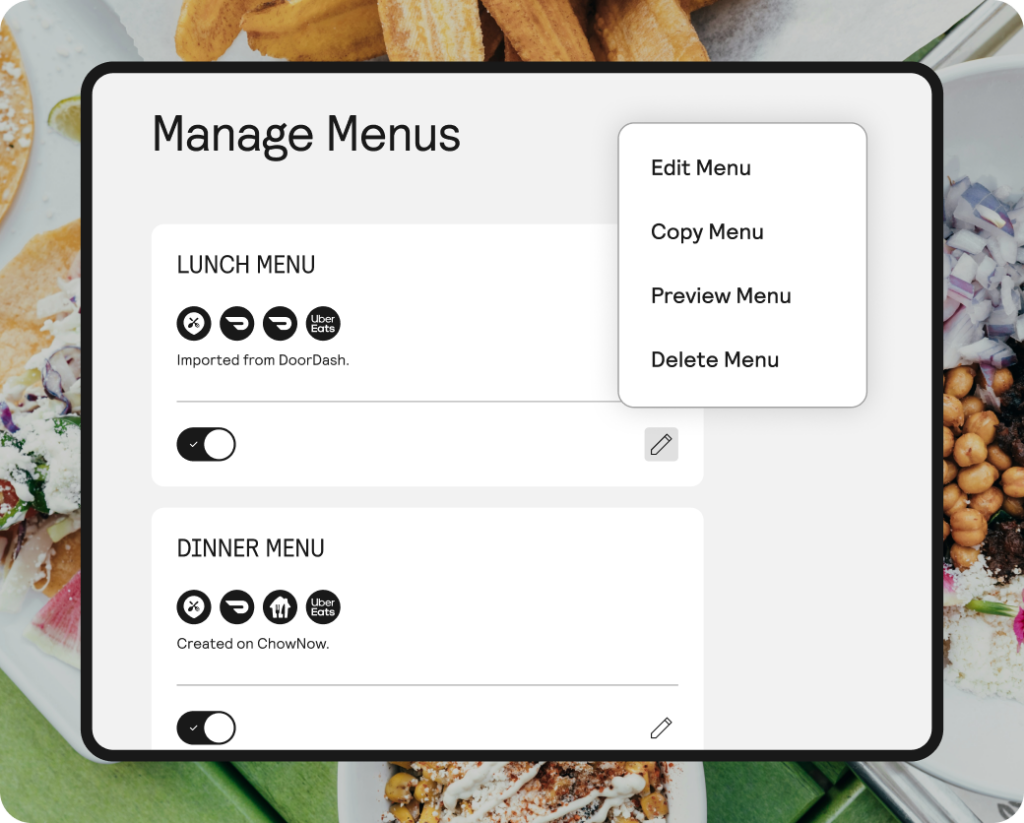
Menu management
- Definition: The process of updating items, prices, modifiers, and availability across ordering channels.
- Example: “We update menu management weekly so online and in store menus match.”
- Why it matters: Clean menu updates prevent wrong orders and reduce refunds and remakes.
Kitchen Display System (KDS)
- Definition: A digital screen that shows tickets in the kitchen, replacing or supporting paper tickets.
- Example: “The KDS helps us see what is firing, what is late, and what is next.”
- Why it matters: It improves speed and accuracy during busy service, especially with online orders.
Delivery dispatch
- Definition: Assigning deliveries to drivers, couriers, or delivery partners and tracking handoff.
- Example: “We use delivery dispatch so orders go out on time and drivers know where to go.”
- Why it matters: Better dispatch reduces late deliveries and protects guest satisfaction.
Pickup vs delivery vs curbside
- Definition: The fulfillment option a guest chooses for their order.
- Example: “We set clear pickup, delivery, and curbside instructions so guests do not get confused.”
- Why it matters: Clear fulfillment options reduce complaints and keep operations predictable.
Prep time (lead time)
- Definition: The time your kitchen needs to prepare an order before it is ready for pickup or delivery.
- Example: “We increased prep time during rush so tickets stop stacking at the pass.”
- Why it matters: Accurate lead time sets expectations and reduces late order stress.
Loyalty program (rewards program)
- Definition: A system that encourages repeat visits by offering points or perks.
- Example: “We use a loyalty program to nudge guests toward add ons and repeat orders.”
- Why it matters: It increases repeat business without relying on constant discounts.
Email marketing
- Definition: Messaging guests through email for updates, promos, and reminders.
- Example: “We send an email when we launch a new menu item or limited time offer.”
- Why it matters: Email drives repeat orders and helps you market outside social platforms.
Restaurant Operations Terms

Average check
- Definition: The average amount spent per guest or party.
- Example: “We want to raise the average check by suggesting sides and drinks that fit the meal.”
- Why it matters: Small increases to average check size can add up fast.By rewarding customers for hitting certain spending thresholds, a loyalty program can incentivize higher spending per order.
Break even
- Definition: The sales level where revenue covers costs and profit is zero.
- Example: “If we do not hit break even by Thursday, we adjust labor and prep.”
- Why it matters: Knowing break even and other restaurant KPIs helps you make smarter staffing and promo decisions.
Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Definition: The cost of ingredients used to make the items you sell.
- Example: “We tracked COGS and found our sauces were driving waste.”
- Why it matters: Lowering food cost supports healthier profit margins without raising prices.
Cross training
- Definition: Training staff to work more than one role.
- Example: “We cross train hosts on phones so the dining room stays covered.”
- Why it matters: Cross training makes scheduling easier and keeps service steady when someone calls out.
Foot traffic
- Definition: How many people pass by or walk into your restaurant.
- Example: “We put a sidewalk sign out to increase foot traffic at lunch.”
- Why it matters: More walk-ins usually means more chances to build regulars.
Inventory turnover
- Definition: How quickly you sell and replace inventory.
- Example: “We improved inventory turnover so produce stops expiring mid week.”
- Why it matters: Better turnover reduces waste and helps cash flow.
Loss leader
- Definition: An item priced low to attract guests, with the goal of selling higher margin add ons.
- Example: “Our taco night is a loss leader, but it boosts beverage sales.”
- Why it matters: Done intentionally, it can increase total sales without harming long term profitability.
Markup
- Definition: The amount added to cost to cover overhead and profit.
- Example: “We reviewed markup on wine so it matches our neighborhood.”
- Why it matters: Smart markup supports margins while staying competitive.
Net profit margin
- Definition: The percentage of revenue left after all expenses are paid.
- Example: “We improved net profit margin by tightening labor and reducing refunds.”
- Why it matters: Margin is the difference between surviving and growing. If you want to increase your margins on takeout order, commission free ordering helps you protect profits without raising prices.
Occupancy cost
- Definition: The total cost of rent, utilities, and related space expenses.
- Example: “We watch occupancy costs to monitor how rent and utilities impact our bottom line.”
- Why it matters: If occupancy gets too high, it limits your ability to invest in staff and marketing.
P&L statement (profit and loss statement)
- Definition: A profit and loss report showing revenue, costs, and expenses over time.
- Example: “We review the P&L monthly to catch rising costs early.”
- Why it matters: It gives you the clearest picture of what is working and what needs attention.
Prime Cost
- Definition: The sum of your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), including food and beverage, plus your total labor costs (wages, salaries, benefits, taxes).
- Example: “We watch prime cost weekly and adjust prep and scheduling when it climbs.”
- Why it matters: Prime cost is one of the fastest levers for improving profitability.
Seasonality
- Definition: Sales changes based on time of year, weather, and local events.
- Example: “We plan for seasonality by staffing up for summer and building winter promos.”
- Why it matters: Planning ahead prevents panic scheduling and last minute discounting.
Yield management
- Definition: Adjusting pricing or availability based on demand to maximize revenue.
- Example: “We use yield management on reservations for peak dining times.”
- Why it matters: It can improve revenue without increasing volume or workload.
Limited time offer (LTO)
- Definition: A menu item or promo only available for a short window to drive urgency.
- Example: “We ran an LTO for a seasonal bowl and promoted it in email and on social media.”
- Why it matters: LTOs can lift traffic during slow periods when planned intentionally. Download the 2026 Restaurant Marketing Calendar for month by month seasonal ideas.
Back of House Restaurant Terms

Back of House (BOH)
- Definition: The kitchen and prep areas guests do not see, where food is made and systems run.
- Example: “BOH updated prep labels and the line moved faster all night.”
- Why it matters: Clear BOH communication reduces mistakes that cost time and food.
86’d
- Definition: A callout that an item is sold out and must stop being sold immediately.
- Example: “We 86’d the salmon, update the servers and the online menu.”
- Why it matters: Accurately marking items as sold out prevents refunds, remakes, and angry guests.
All day
- Definition: The total number of an item needed across all open tickets right now.
- Example: “We need three steaks all day, meaning three total on the rail.”
- Why it matters: It helps the line stay coordinated during a rush.
Behind
- Definition: A safety call when moving behind someone.
- Example: “Behind! Hot pan coming through.”
- Why it matters: It prevents collisions and injuries in tight kitchens.
Burner
- Definition: Slang for an extremely busy shift.
- Example: “It is a burner tonight.”
- Why it matters: Calling it early helps the team pace, prep, and communicate.
Call
- Definition: Announcing orders or instructions out loud so the team stays synced.
- Example: “Calling two burgers medium rare, one pasta.”
- Why it matters: Good calls reduce missed tickets and refires.
Covers
- Definition: The number of guests served or expected in a shift.
- Example: “We are at 120 covers tonight, prep extra fries.”
- Why it matters: Covers inform staffing, prep, and pacing.
Daydots
- Definition: Date or day labels used for food rotation and freshness.
- Example: “Check the daydots on the sauce before service.”
- Why it matters: It reduces waste and protects food safety.
Dead plate
- Definition: Food that has sat too long and needs to be remade.
- Example: “That burger is a dead plate, refire it.”
- Why it matters: Catching it early protects the guest experience.
Deuce
- Definition: Slang for a table of two.
- Example: “We have a deuce waiting for appetizers.”
- Why it matters: It speeds up communication without stopping the line.
Fire
- Definition: The command to start cooking a specific course or table.
- Example: “Fire table six mains now.”
- Why it matters: Correct timing keeps FOH and BOH aligned.
Flash
- Definition: Quickly reheat or finish a dish, often under a broiler.
- Example: “Flash that lasagna, it is not hot enough.”
- Why it matters: It saves a ticket without restarting the whole dish.
Meez
- Definition: Short for mise en place, your station setup and prepped ingredients.
- Example: “Make sure your meez is set before doors open.”
- Why it matters: Strong meez prevents chaos once tickets start.
On the fly
- Definition: An urgent request to rush a dish due to an issue or delay.
- Example: “Caesar on the fly, the first one got sent back.”
- Why it matters: It helps recover service without derailing the full board.
Post common kitchen slang near the pass for quick reference.
Pass
- Definition: The handoff area where plates are checked and sent to the dining room.
- Example: “Bring it to the pass, expo will run it.”
- Why it matters: The pass is quality control during peak volume.
Rail
- Definition: Where tickets line up for the kitchen to execute.
- Example: “The rail is full, we are slammed.”
- Why it matters: It is the visual heartbeat of the shift.
Sharp
- Definition: A safety call when carrying or handing off a knife.
- Example: “Sharp, coming through.”
- Why it matters: It prevents injuries during fast movement.
Stage
- Definition: A trial shift where a cook works to learn and be evaluated.
- Example: “We have a stage in the pantry tonight.”
- Why it matters: It helps you hire well and protect standards.
5 out
- Definition: A call that something is about five minutes from happening.
- Example: “Table 12 is 5 out, get dessert menus ready.”
- Why it matters: It improves timing between the kitchen and the floor.
Cooked to order
- Definition: Food prepared based on a guest request at the time of ordering.
- Example: “Steaks are cooked to order, confirm temp on the ticket.”
- Why it matters: It protects quality and reduces remakes.
Front of House Restaurant Terms

Front of house (FOH)
- Definition: The guest facing areas and the team that serves diners.
- Example: “FOH will review pacing and sections before doors open.”
- Why it matters: FOH controls the guest experience and service flow.
Comp
- Definition: Giving a guest something free, often to resolve an issue.
- Example: “Comp the dessert for that long wait.”
- Why it matters: Used wisely, comps save relationships and protect reviews.
Double seating
- Definition: Seating two tables in the same server section back to back.
- Example: “You are double sat, greet both tables fast.”
- Why it matters: It affects pacing, ticket timing, and guest satisfaction.
Four top, Two top
- Definition: A table setup for four guests or two guests.
- Example: “Set a four top near the window.”
- Why it matters: Clear table language speeds up turns and seating.
Greeter
- Definition: The person who welcomes guests and sets the tone.
- Example: “Greeter, let them know the wait time and offer the bar.”
- Why it matters: A strong first touch reduces walkouts and no shows.
No show
- Definition: A reservation that does not arrive and was not canceled.
- Example: “That eight top is a no show, release the table.”
- Why it matters: It impacts revenue, staffing, and table turn planning.
Pivot point
- Definition: A reference seat used to track orders around a table.
- Example: “Use seat one as the pivot point so food lands correctly.”
- Why it matters: It reduces wrong plates and remakes.
Pre bussing
- Definition: Clearing plates and clutter while guests are still seated.
- Example: “Pre buss table 4 before dessert.”
- Why it matters: It makes turns faster and keeps the dining room clean.

Runner
- Definition: A staff member who delivers food from the kitchen to tables.
- Example: “Runner, take these mains to table 6.”
- Why it matters: It speeds service and keeps servers with their guests.
Table turn
- Definition: The full cycle of seat, serve, and reset for the next guests.
- Example: “We are targeting a 45 minute table turn at lunch.”
- Why it matters: Faster turns can increase revenue without more seats.
Tip out
- Definition: Sharing a portion of tips with support staff.
- Example: “Tip out the bartender and busser after close.”
- Why it matters: It keeps teamwork fair and consistent.
Top off
- Definition: Refilling a guest drink without being asked.
- Example: “Top off water for table 5.”
- Why it matters: Small touches improve reviews and repeat visits.
Turn and burn
- Definition: Moving guests through quickly to free tables.
- Example: “We are turning and burning tonight, keep pacing tight.”
- Why it matters: It increases throughput but needs care to avoid rushed vibes.
Upsell
- Definition: Suggesting an add on or higher value item to increase the check.
- Example: “Would you like to add a side salad or upgrade the spirit?”
- Why it matters: Upsells can lift average checks without adding more covers.
Make These Restaurant Terms Work for Your Team
Restaurant terms are not just slang, they are how teams stay coordinated during busy service. This glossary covers restaurant technology terms, restaurant operations terms, and essential FOH and BOH restaurant language that helps you communicate clearly, train faster, and avoid mistakes that cost time and money.
Turn these concepts into action with a plan. Download the 2026 Restaurant Marketing Calendar for a month by month roadmap of promotions designed to drive more direct orders.
And when you are ready to turn more of those promotions into direct, repeat orders, ChowNow can help you protect margins, build diner loyalty, and keep your brand front and center. If you want to see what ChowNow can do for your restaurant, book a demo.
Frequently Asked Questions About Restaurant Terminology
What is the difference between first party and third party online ordering?
First party ordering is when guests order directly from your restaurant, while third party ordering runs through a marketplace that may charge commission fees and limit customer data ownership.
What is order aggregation and why does it matter?
Order aggregation consolidates orders from multiple channels into one place, which helps teams avoid missed tickets, reduce tablet clutter, and keep service smoother.
What is prime cost and what should it be?
Prime cost is your COGS plus labor. Many operators aim to keep prime cost under 60 percent, but the right target depends on your concept, location, and service model.
What does all day mean in a kitchen?
All day means the total number of an item needed across all open tickets right now, not just on one ticket, so the line can stay coordinated during a rush.
What does 86d mean in restaurant slang?
86d means an item is sold out and must stop being sold immediately. It can also refer to removing something from service.
What is an average check and how do you increase it?
Average check is the average amount guests spend per order. Operators increase it through smart upsells, bundles, and loyalty rewards that encourage spending thresholds.